Medieval Leprosy
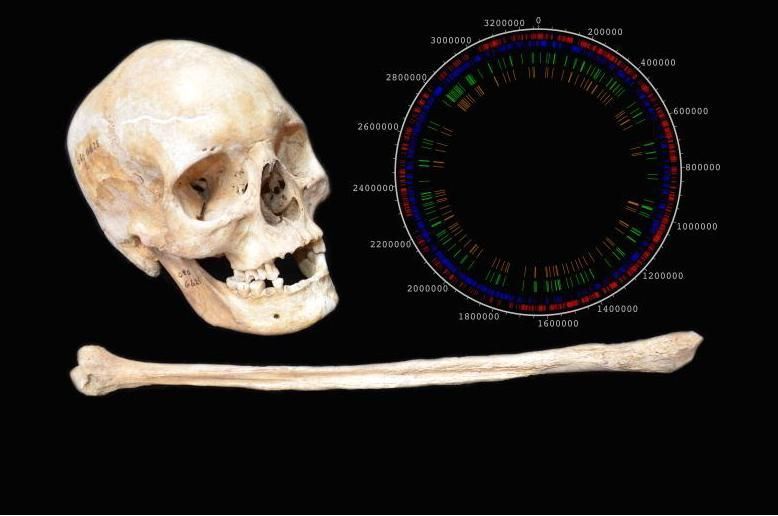
Researchers have reconstructed the entire genome of Medieval-era leprosy bacteria.


LESSONS FROM THE DEAD - Scientists attempt to bring back an extinct frog. Mummies showing signs of heart disease make researchers rethink assumptions about lifestyle and diet. The mysterious death zone within African "fairy circles" explained. Also: a miniature laboratory under the skin monitors blood chemistry.
Did our ability to digest alcohol first emerge at the dawn of civilization or millions of years earlier?
Ancient people had beneficial bacteria to fight dental plaque that is absent in modern populations.
Other people help human mothers through the emotional and physical aspects of the birth process, which help decrease the risks of childbirth. But apes have easy births, and prefer to go it alone.
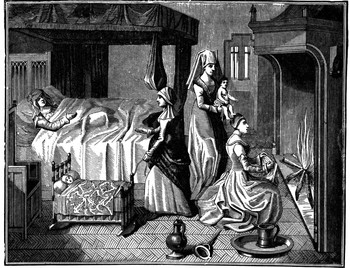
Other people help human mothers through the emotional and physical aspects of the birth process, which help decrease the risks of childbirth. But apes have easy births, and prefer to go it alone.
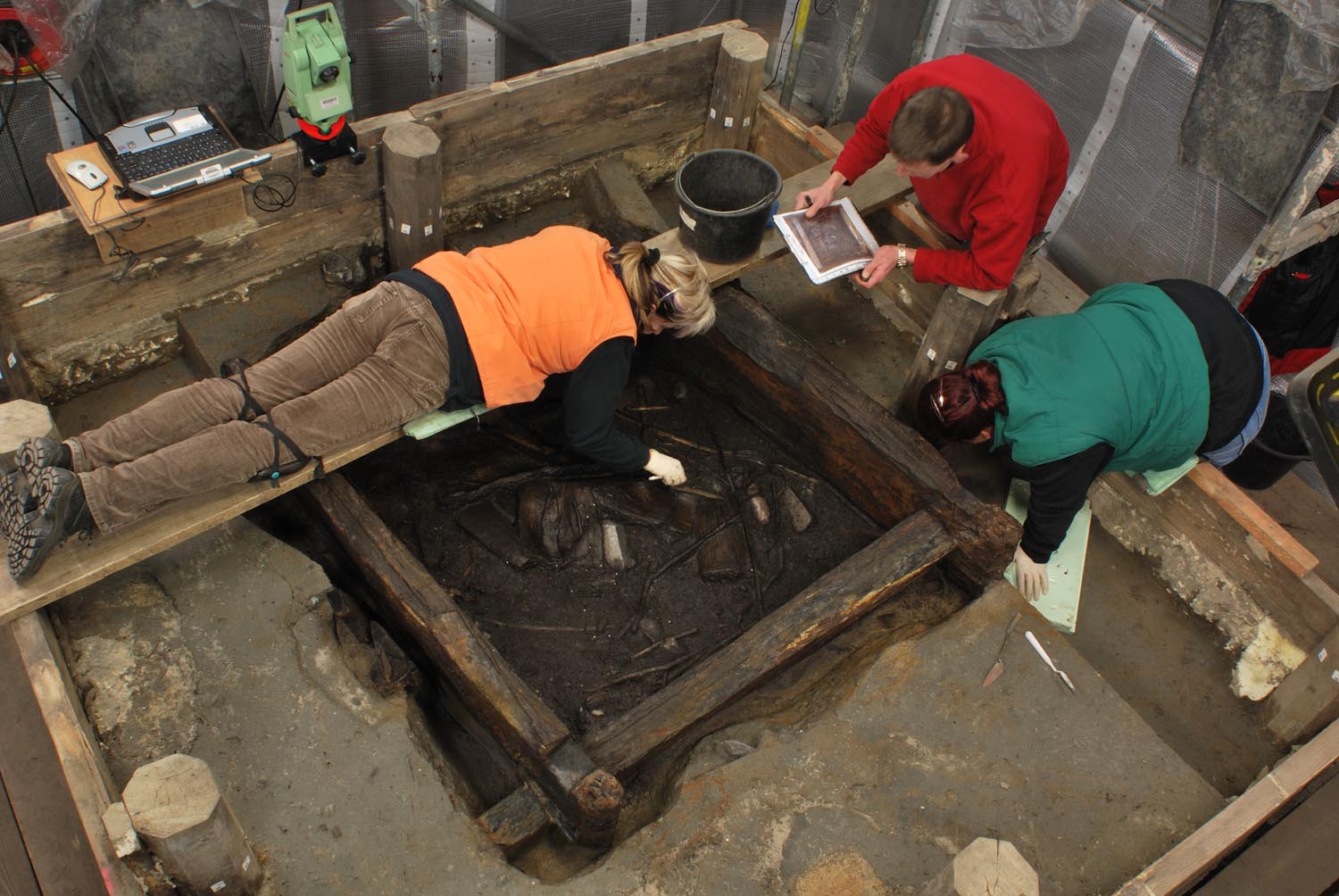

The discovery of ancient wooden wells in Germany reveals that Neolithic woodworking was more sophisticated than previously believed.
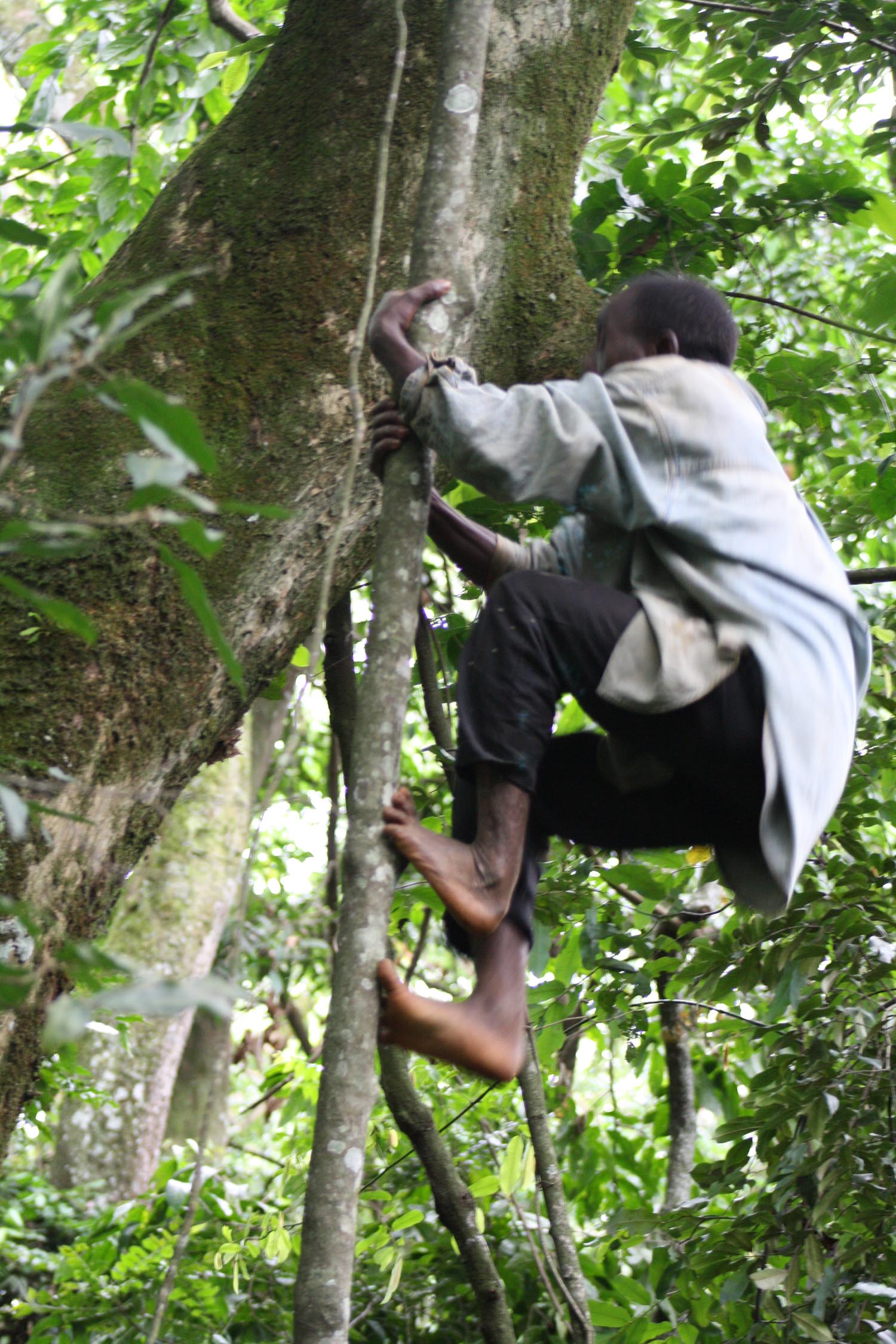

The Twa people of Uganda climb trees with ease. A new study suggests that the trait may be the result of practical necessity.


CHILD DEVELOPMENT - Are kids naturally stingy? Why children's self-control could depend on the adults around them. And why math anxiety "hurts". Also: What monsters from Dungeons & Dragons can tell us about the importance of eyes.

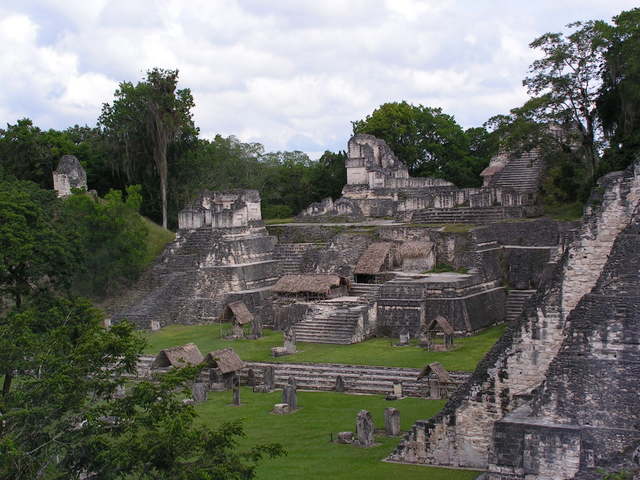
Sophisticated computer imaging may help decode the world's oldest un-deciphered written language.

BIRDS, BUTTERFLIES & BEETLES - How radar helped solve a migration mystery, why malaria could be heading north, and how dung beetles cool themselves off. Also: a 21st century technology that's helping archaeologists crack an ancient code.

The incidence of autism has increased in recent years, and so have efforts to identify and treat it earlier.
Monsters from the role playing game “Dungeons & Dragons” help reveal what’s most important to us.

SURVIVAL - Why female Komodo dragons die young, a whale that sounded like a person, and algae that flee their predators. Also: how the brain's insulation differs between us and chimpanzees, and why that insulation is so important to social development.
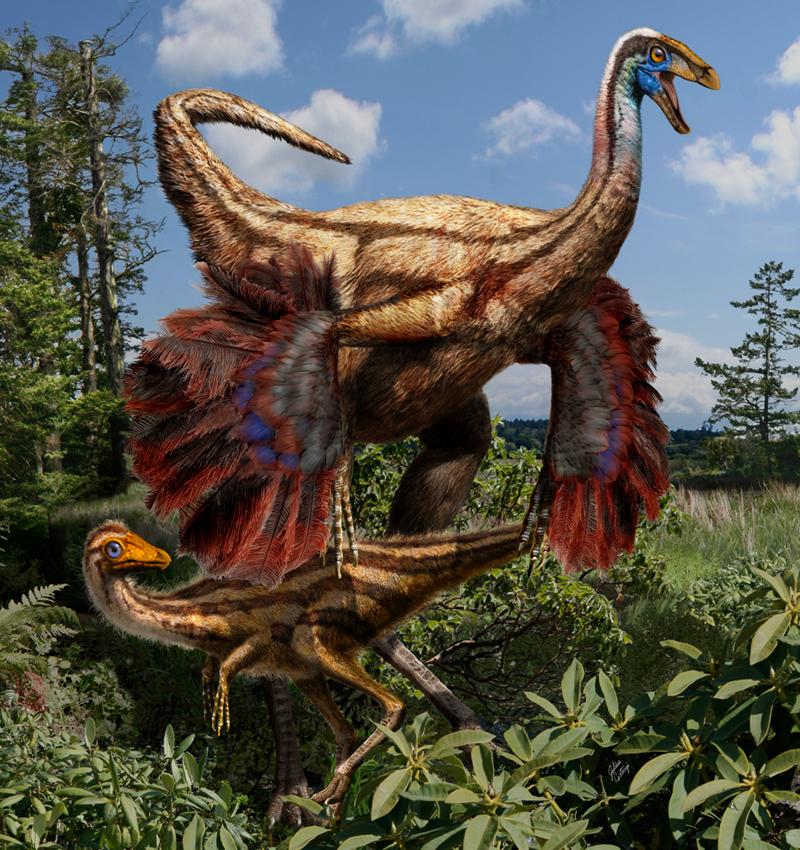

Evidence suggests that an ancestor of modern humans both walked upright and climbed trees.
Over several centuries in Imperial Korea, eunuchs far outlived their non-castrated counterparts.

MEDICAL BREAKTHROUGHS - A new drug that could block heroin addiction, how mice could speed up AIDS research, and why we're more prone to cancer than our closest living relatives. Also: the two brain chemicals behind sleep paralysis.

People living as hunter-gatherers burn roughly as many calories per day as those in industrialized countries.

Traces of milk fat in pottery confirm that prehistoric North Africans practiced dairy farming.

The link between touch and hearing. And, why bilinguals hear better in noisy environments. Also: new brain research could illuminate why we’re willing to share so much personal information on social networking sites. And, how much money would it take for you to give someone an electric shock? The answer may surprise you.

How the brain's reward system makes sharing personal information on social media so compelling.

People who live around fewer varieties of plants, and whose skin carries fewer kinds of bacteria, are more likely to have allergies.
