Podcast: Play in new window
BOB HIRSHON (host):
Sizing up earth’s tilt. I’m Bob Hirshon and this is Science Update.
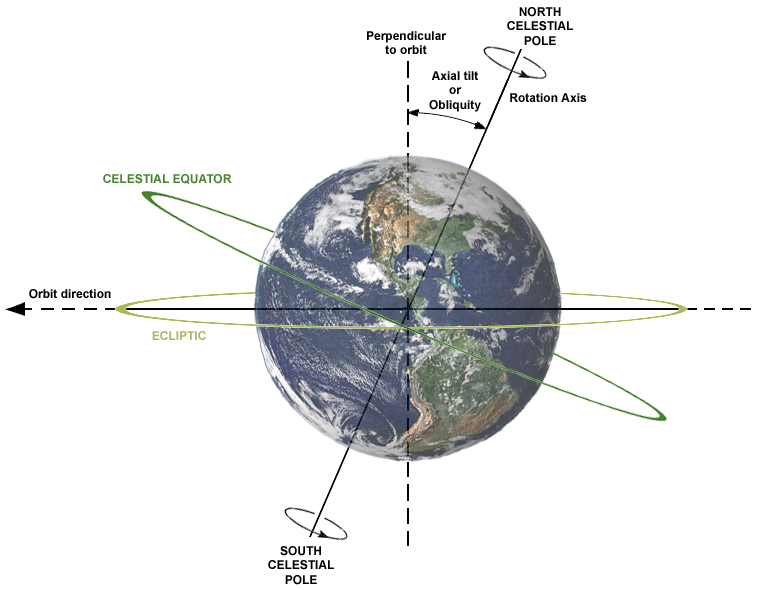
The earth tilts about 23.4 degrees—in the summer months, the north pole is tilted toward the sun, giving us more daylight and warmth, and in the winter, it’s tilted away. Tyler from Missouri emailed us to ask how scientists know that angle. NASA Physicist Betsy Pugel says that if you’re willing to wait until noon at the winter solstice—December 21st—you can measure it yourself by standing a ruler outside on the ground.
BETSY PUGEL (NASA):
Just take the length of the ruler, divide it by the length of the shadow, and then go into a calculator and calculate the inverse tangent and it will give you what that angle is. And so that angle is related to the tilt of the earth where you are.
HIRSHON:
She adds that thousands of years ago, people worked out the tilt in much the same way, but without the calculator. I’m Bob Hirshon for AAAS, the Science Society.
————————————————————————————————————————————————————-
CALCULATE EARTH’S TILT ON DECEMBER 21st USING BETSY PUGEL’S HANDY EARTH TILT CALCULATOR!
Click here for a printable version of the instructions
Why take other people’s word for it that Earth has a tilt? Measure it for yourself on December 21st!
Tools:
- A stick-like object (For example: a stick; a ruler; a meter stick; a broom handle) to stick into the ground
- Tape measure or ruler/meter stick for measuring
- Pen/Pencil/Crayon and paper (to record your data)
- Graph paper (attached to this document)
- Calculator or the internet and search engine (as your alternate calculator)
- Warm clothes to brave the weather a few times throughout the day to make measurements
Note: This will not work if it is a cloudy day.
Note #2: This method works in places that are north of the “Tropic of Cancer,” which includes the Continental U.S. and Canada, Europe, most of Asia and the northernmost part of Africa.
Two approaches:
(1) The Quick and Easy Version, which will take about 10 minutes max
(2) Winter Solstice Tilt Measurement, The Extended Remix, takes a few hours, but makes you feel like a boss (science-style)
Directions:
(1) Check the table below for your time zone (assuming US conventions here).
- If you are doing The Quick and Dirty Version, make sure that you’ve been able to set everything up about 10 minutes before the official solstice time.
- If you are doing The Extended Remix, prepare everything to start 1 hour before the solstice time and allow for an hour after the solstice takes place
(2) Find out your latitude (you can use a search engine to do this for you) or use our table to roughly identify where your latitude is.
(3) Find some level ground and place the stick in the ground (or snow) so that the stick is vertical and so that you are able to measure the shadow that it casts. It’s important that you are able to see the shadow for all of your measurements.
(4) Measure the length of the stick above the ground. Write the length on the piece of paper.
(5) Note the time and write that on your piece of paper.
(6) Measure the length of the shadow of the stick.
(7) If you are doing The Quick and Dirty Version, jump to the end of the instructions, where it says How do I calculate tilt?
(8) If you are doing The Extended Remix, you’ll need to note the time and the length of the shadow every 10 minutes from one hour before the start of solstice to one hour after the time passes. You will end up with 6 data points in the first hour: the solstice point and 6 data points after the solstice takes place.
Extended Remix Version:
(1) If you do (8) as instructed, you will be able to plot the length of the shadow versus time using the graph paper
(2) The graph should look something like this:
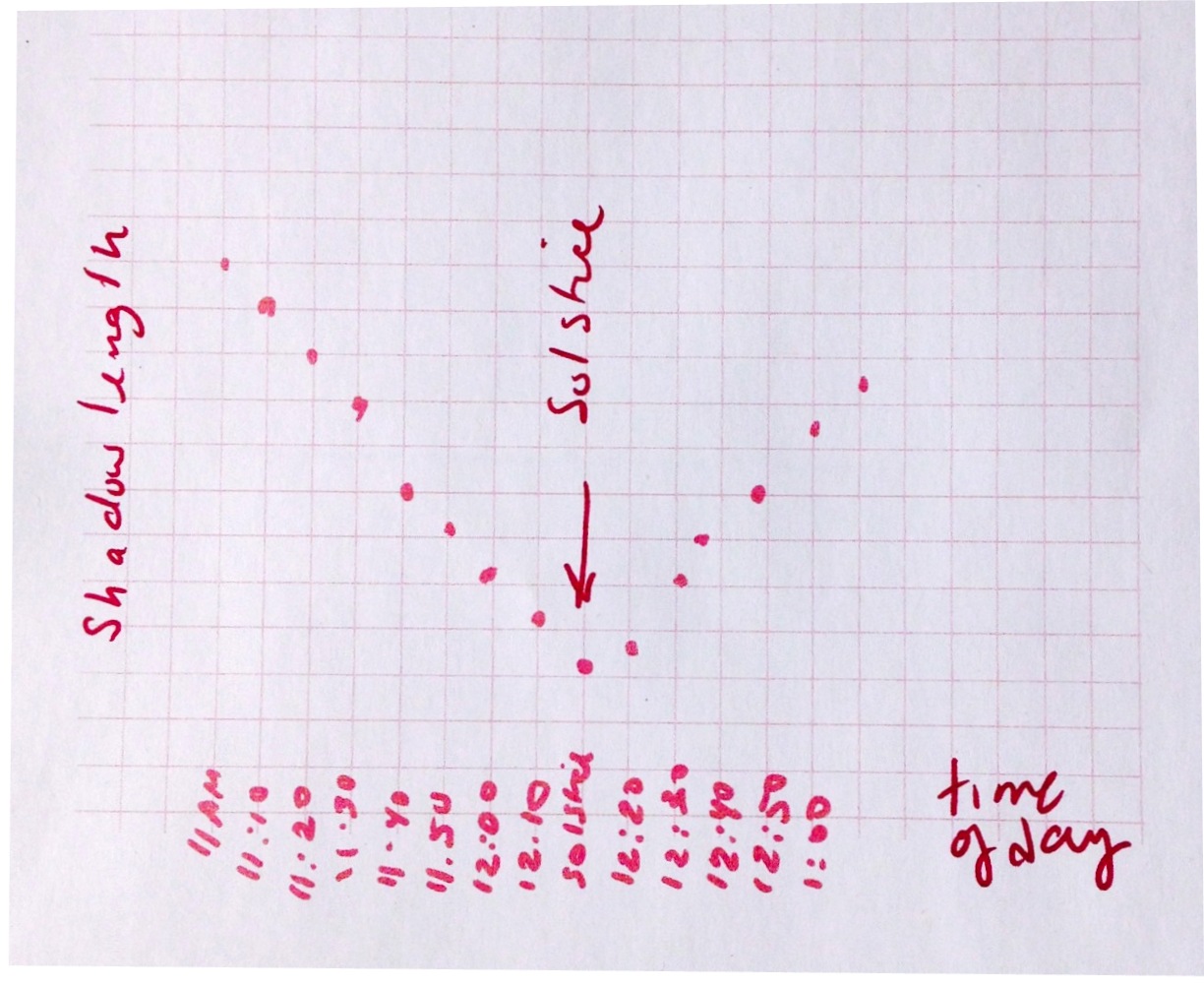
How Do I Calculate Tilt?:
You’ll need:
- a handheld calculator or a computer calculator with the tan-1 button on it,
- or
- https://www.rapidtables.com/calc/math/Arctan_Calculator.htm
For the Quick and Dirty Version:
(1) Using any calculator, calculate the following: (Stick Length)/(Shadow Length). Make sure that your answer is in degrees. We’ll call this the Sun’s Angle.
(2) Subtract this number from your latitude: (Your Latitude) – (Sun’s Angle) = Earth’s Tilt
(3) Tada!
For the Extended Remix
(1) Select the shadow length at the solstice. It should be when the shadow of the stick is the shortest
(2) Using any calculator, calculate the following: (Stick Length)/(Shadow Length). Make sure that your answer is in degrees. We’ll call this the Sun’s Angle.
(3) Subtract this number from your latitude: (Your Latitude) – (Sun’s Angle) = Earth’s Tilt
(4) Tada!
2013 Winter Solstice (December 21st) Time in U.S. time zones :
Eastern Time Zone: 12:11 PM
Central Time Zone: 11:11 AM
Mountain Time Zone: 10:11 AM
Pacific Time Zone: 9:11 AM
Latitude Table (from factmonster.com)
|
Lat. n. |
Long. w. |
|
|||
| City |
° |
‘ |
° |
‘ |
Time |
| Albany, N.Y. |
42 |
40 |
73 |
45 |
12:00 noon |
| Albuquerque, N.M. |
35 |
05 |
106 |
39 |
10:00 a.m. |
| Amarillo, Tex. |
35 |
11 |
101 |
50 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Anchorage, Alaska |
61 |
13 |
149 |
54 |
8:00 a.m. |
| Atlanta, Ga. |
33 |
45 |
84 |
23 |
12:00 noon |
| Austin, Tex. |
30 |
16 |
97 |
44 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Baker, Ore. |
44 |
47 |
117 |
50 |
9:00 a.m. |
| Baltimore, Md. |
39 |
18 |
76 |
38 |
12:00 noon |
| Bangor, Maine |
44 |
48 |
68 |
47 |
12:00 noon |
| Birmingham, Ala. |
33 |
30 |
86 |
50 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Bismarck, N.D. |
46 |
48 |
100 |
47 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Boise, Idaho |
43 |
36 |
116 |
13 |
10:00 a.m. |
| Boston, Mass. |
42 |
21 |
71 |
5 |
12:00 noon |
| Buffalo, N.Y. |
42 |
55 |
78 |
50 |
12:00 noon |
| Calgary, Alba., Can. |
51 |
1 |
114 |
1 |
10:00 a.m. |
| Carlsbad, N.M. |
32 |
26 |
104 |
15 |
10:00 a.m. |
| Charleston, S.C. |
32 |
47 |
79 |
56 |
12:00 noon |
| Charleston, W. Va. |
38 |
21 |
81 |
38 |
12:00 noon |
| Charlotte, N.C. |
35 |
14 |
80 |
50 |
12:00 noon |
| Cheyenne, Wyo. |
41 |
9 |
104 |
52 |
10:00 a.m. |
| Chicago, Ill. |
41 |
50 |
87 |
37 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Cincinnati, Ohio |
39 |
8 |
84 |
30 |
12:00 noon |
| Cleveland, Ohio |
41 |
28 |
81 |
37 |
12:00 noon |
| Columbia, S.C. |
34 |
0 |
81 |
2 |
12:00 noon |
| Columbus, Ohio |
40 |
0 |
83 |
1 |
12:00 noon |
| Dallas, Tex. |
32 |
46 |
96 |
46 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Denver, Colo. |
39 |
45 |
105 |
0 |
10:00 a.m. |
| Des Moines, Iowa |
41 |
35 |
93 |
37 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Detroit, Mich. |
42 |
20 |
83 |
3 |
12:00 noon |
| Dubuque, Iowa |
42 |
31 |
90 |
40 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Duluth, Minn. |
46 |
49 |
92 |
5 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Eastport, Maine |
44 |
54 |
67 |
0 |
12:00 noon |
| Edmonton, Alb., Can. |
53 |
34 |
113 |
28 |
10:00 a.m. |
| El Centro, Calif. |
32 |
38 |
115 |
33 |
9:00 a.m. |
| El Paso, Tex. |
31 |
46 |
106 |
29 |
10:00 a.m. |
| Eugene, Ore. |
44 |
3 |
123 |
5 |
9:00 a.m. |
| Fargo, N.D. |
46 |
52 |
96 |
48 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Flagstaff, Ariz. |
35 |
13 |
111 |
41 |
10:00 a.m. |
| Fort Worth, Tex. |
32 |
43 |
97 |
19 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Fresno, Calif. |
36 |
44 |
119 |
48 |
9:00 a.m. |
| Grand Junction, Colo. |
39 |
5 |
108 |
33 |
10:00 a.m. |
| Grand Rapids, Mich. |
42 |
58 |
85 |
40 |
12:00 noon |
| Havre, Mont. |
48 |
33 |
109 |
43 |
10:00 a.m. |
| Helena, Mont. |
46 |
35 |
112 |
2 |
10:00 a.m. |
| Honolulu, Hawaii |
21 |
18 |
157 |
50 |
7:00 a.m. |
| Hot Springs, Ark. |
34 |
31 |
93 |
3 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Houston, Tex. |
29 |
45 |
95 |
21 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Idaho Falls, Idaho |
43 |
30 |
112 |
1 |
10:00 a.m. |
| Indianapolis, Ind. |
39 |
46 |
86 |
10 |
12:00 noon |
| Jackson, Miss. |
32 |
20 |
90 |
12 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Jacksonville, Fla. |
30 |
22 |
81 |
40 |
12:00 noon |
| Juneau, Alaska |
58 |
18 |
134 |
24 |
8:00 a.m. |
| Kansas City, Mo. |
39 |
6 |
94 |
35 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Key West, Fla. |
24 |
33 |
81 |
48 |
12:00 noon |
| Kingston, Ont., Can. |
44 |
15 |
76 |
30 |
12:00 noon |
| Klamath Falls, Ore. |
42 |
10 |
121 |
44 |
9:00 a.m. |
| Knoxville, Tenn. |
35 |
57 |
83 |
56 |
12:00 noon |
| Las Vegas, Nev. |
36 |
10 |
115 |
12 |
9:00 a.m. |
| Lewiston, Idaho |
46 |
24 |
117 |
2 |
9:00 a.m. |
| Lincoln, Neb. |
40 |
50 |
96 |
40 |
11:00 a.m. |
| London, Ont., Can. |
43 |
2 |
81 |
34 |
12:00 noon |
| Long Beach, Calif. |
33 |
46 |
118 |
11 |
9:00 a.m. |
| Los Angeles, Calif. |
34 |
3 |
118 |
15 |
9:00 a.m. |
| Louisville, Ky. |
38 |
15 |
85 |
46 |
12:00 noon |
| Manchester, N.H. |
43 |
0 |
71 |
30 |
12:00 noon |
| Memphis, Tenn. |
35 |
9 |
90 |
3 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Miami, Fla. |
25 |
46 |
80 |
12 |
12:00 noon |
| Milwaukee, Wis. |
43 |
2 |
87 |
55 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Minneapolis, Minn. |
44 |
59 |
93 |
14 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Mobile, Ala. |
30 |
42 |
88 |
3 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Montgomery, Ala. |
32 |
21 |
86 |
18 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Montpelier, Vt. |
44 |
15 |
72 |
32 |
12:00 noon |
| Montreal, Que., Can. |
45 |
30 |
73 |
35 |
12:00 noon |
| Moose Jaw, Sask., Can. |
50 |
37 |
105 |
31 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Nashville, Tenn. |
36 |
10 |
86 |
47 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Nelson, B.C., Can. |
49 |
30 |
117 |
17 |
9:00 a.m. |
| Newark, N.J. |
40 |
44 |
74 |
10 |
12:00 noon |
| New Haven, Conn. |
41 |
19 |
72 |
55 |
12:00 noon |
| New Orleans, La. |
29 |
57 |
90 |
4 |
11:00 a.m. |
| New York, N.Y. |
40 |
47 |
73 |
58 |
12:00 noon |
| Nome, Alaska |
64 |
25 |
165 |
30 |
8:00 a.m. |
| Oakland, Calif. |
37 |
48 |
122 |
16 |
9:00 a.m. |
| Oklahoma City, Okla. |
35 |
26 |
97 |
28 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Omaha, Neb. |
41 |
15 |
95 |
56 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Ottawa, Ont., Can. |
45 |
24 |
75 |
43 |
12:00 noon |
| Philadelphia, Pa. |
39 |
57 |
75 |
10 |
12:00 noon |
| Phoenix, Ariz. |
33 |
29 |
112 |
4 |
10:00 a.m. |
| Pierre, S.D. |
44 |
22 |
100 |
21 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Pittsburgh, Pa. |
40 |
27 |
79 |
57 |
12:00 noon |
| Portland, Maine |
43 |
40 |
70 |
15 |
12:00 noon |
| Portland, Ore. |
45 |
31 |
122 |
41 |
9:00 a.m. |
| Providence, R.I. |
41 |
50 |
71 |
24 |
12:00 noon |
| Quebec, Que., Can. |
46 |
49 |
71 |
11 |
12:00 noon |
| Raleigh, N.C. |
35 |
46 |
78 |
39 |
12:00 noon |
| Reno, Nev. |
39 |
30 |
119 |
49 |
9:00 a.m. |
| Richfield, Utah |
38 |
46 |
112 |
5 |
10:00 a.m. |
| Richmond, Va. |
37 |
33 |
77 |
29 |
12:00 noon |
| Roanoke, Va. |
37 |
17 |
79 |
57 |
12:00 noon |
| Sacramento, Calif. |
38 |
35 |
121 |
30 |
9:00 a.m. |
| St. John, N.B., Can. |
45 |
18 |
66 |
10 |
1:00 p.m. |
| St. Louis, Mo. |
38 |
35 |
90 |
12 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Salt Lake City, Utah |
40 |
46 |
111 |
54 |
10:00 a.m. |
| San Antonio, Tex. |
29 |
23 |
98 |
33 |
11:00 a.m. |
| San Diego, Calif. |
32 |
42 |
117 |
10 |
9:00 a.m. |
| San Francisco, Calif. |
37 |
47 |
122 |
26 |
9:00 a.m. |
| San Jose, Calif. |
37 |
20 |
121 |
53 |
9:00 a.m. |
| San Juan, P.R. |
18 |
30 |
66 |
10 |
1:00 p.m. |
| Santa Fe, N.M. |
35 |
41 |
105 |
57 |
10:00 a.m. |
| Savannah, Ga. |
32 |
5 |
81 |
5 |
12:00 noon |
| Seattle, Wash. |
47 |
37 |
122 |
20 |
9:00 a.m. |
| Shreveport, La. |
32 |
28 |
93 |
42 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Sioux Falls, S.D. |
43 |
33 |
96 |
44 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Sitka, Alaska |
57 |
10 |
135 |
15 |
8:00 a.m. |
| Spokane, Wash. |
47 |
40 |
117 |
26 |
9:00 a.m. |
| Springfield, Ill. |
39 |
48 |
89 |
38 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Springfield, Mass. |
42 |
6 |
72 |
34 |
12:00 noon |
| Springfield, Mo. |
37 |
13 |
93 |
17 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Syracuse, N.Y. |
43 |
2 |
76 |
8 |
12:00 noon |
| Tampa, Fla. |
27 |
57 |
82 |
27 |
12:00 noon |
| Toledo, Ohio |
41 |
39 |
83 |
33 |
12:00 noon |
| Toronto, Ont., Can. |
43 |
40 |
79 |
24 |
12:00 noon |
| Tulsa, Okla. |
36 |
09 |
95 |
59 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Vancouver, B.C., Can. |
49 |
13 |
123 |
06 |
9:00 a.m. |
| Victoria, B.C., Can. |
48 |
25 |
123 |
21 |
9:00 a.m. |
| Virginia Beach, Va. |
36 |
51 |
75 |
58 |
12:00 noon |
| Washington, D.C. |
38 |
53 |
77 |
02 |
12:00 noon |
| Wichita, Kan. |
37 |
43 |
97 |
17 |
11:00 a.m. |
| Wilmington, N.C. |
34 |
14 |
77 |
57 |
12:00 noon |
| Winnipeg, Man., Can. |
49 |
54 |
97 |
7 |
11:00 a.m |
